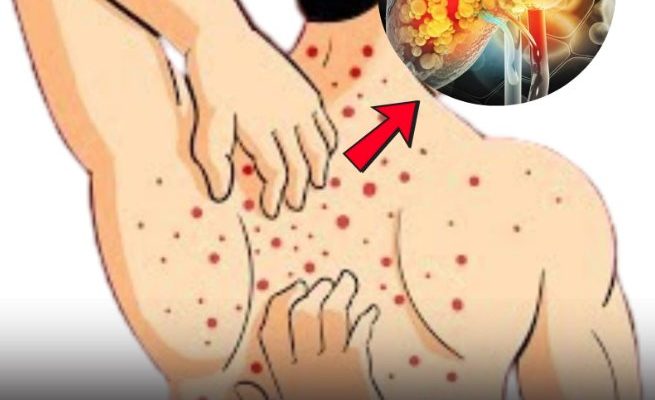
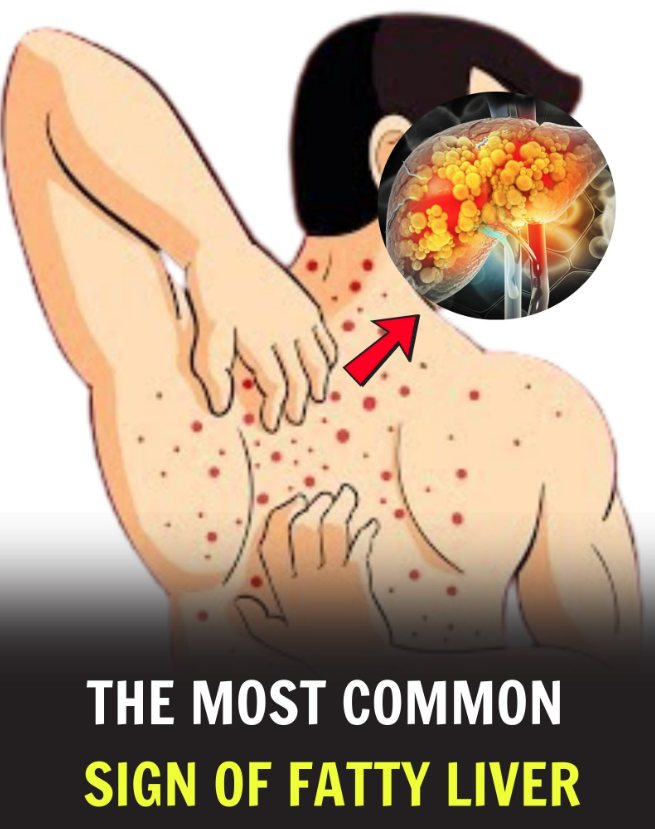
Fatty liver disease, also known as hepatic steatosis, occurs when excess fat accumulates in the liver, affecting its ability to function properly. While poor lifestyle choices, obesity, and metabolic disorders are leading causes, early detection and proactive management can help prevent serious complications.
This guide will explore the causes, symptoms, types, and lifestyle strategies that can help prevent and manage fatty liver disease effectively.
Understanding Fatty Liver Disease
Your liver is responsible for filtering toxins, metabolizing fats, and regulating essential nutrients in the body. When excess fat builds up, it can lead to inflammation, scarring, and eventually liver damage.
Fatty liver disease is increasingly common, especially among those with unhealthy diets, sedentary lifestyles, or excessive alcohol consumption. Understanding its risk factors and symptoms is key to preventing progression to more severe liver conditions.
What Causes Fatty Liver?
Several factors contribute to fat buildup in the liver, including:
1. Unhealthy Diet
Consuming processed foods, high-sugar drinks, and unhealthy fats increases the risk of fatty liver. A diet lacking in fiber, lean proteins, and healthy fats can also contribute to the problem.
2. Obesity
Being overweight or obese is a major risk factor, as excess body fat increases the accumulation of fat in the liver, leading to inflammation and damage.
3. Insulin Resistance
Individuals with type 2 diabetes or metabolic syndrome often have insulin resistance, which increases fat storage in the liver and disrupts its normal function.
4. Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Heavy and prolonged alcohol consumption causes alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD) by impairing the liver’s ability to break down fats.
5. Genetics
Certain individuals have a genetic predisposition to developing fatty liver disease, even if they follow a healthy lifestyle.
6. Pregnancy
In rare cases, women develop acute fatty liver of pregnancy (AFLP), which usually resolves after childbirth.
Symptoms of Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease is often silent in its early stages, making it difficult to detect without medical tests. However, some common symptoms include: